Characteristics
Features of Industry Which Influence the Pharmaceutical Packaging
Content
•
Definition Of Packaging
•
Industrial Packaging Market Outlook.
•
Stability Testing and
Compatibility Testing Of Packaging Materials.
•
Stage S in the Development of a Package Product Combination.
•
Qualification and Quality Control of Packaging
Components.
•
Standard and Specialty Packaging Solution for the
Pharmaceutical Industry.
Packaging:
•
Packaging means the wrapping or bottling of products to make
them safe from damages during transportation and storage. It keeps a product
safe and marketable and helps in identifying, describing, and promoting the
product.
•
“Packing is the preparation of product or commodity for
proper storage and/or transportation. It may entail blocking, marking, sealing,
strapping, weather proofing, wrapping, etc.”
Industrial Packaging Market Outlook
•
Global industrial packaging market size was valued at 53,743
million in 2016, and is expected to garner 69,787 million by 2023. Industrial
goods are heavy, bulky, and sensitive to external atmosphere.
•
Thus it is necessary
to conserve the product for longer time during storage and transportation
specifically with hermetically sealed packaging and secured from external
contamination.
•
Rise in building and construction activities in majority of
the emerging economics especially in India and china. Rise in food and beverages
industry to meet the demand of growing population and rapid growth of exports,
which requires superior packaging standards for the international market are
the major factors that are expected to the market growth during forecast
period.
•
In the global pharmaceutical industry, the efficient
transport of drugs not only depends on the means of storage and mobility but
primarily on the packaging of the drug. However, there are a few factors common
to pharmaceutical packaging irrespective of the product’s classification.
•
The packaging standard required in the pharmaceutical
industry is superior to other industries because pharma packagers need to
maintain product standards and quality, which includes the requirements of
uniformity, purity, side effects, shelf life, safety, integrity, and
efficiency, among others.
•
Manufacturers must possess an in-depth understanding of every
characteristic of the product, including formulation, dosage form, physical and
chemical properties. That information needs to be amalgamated with
manufacturing, packaging, marketing, distribution, product end use and
profitability projections.
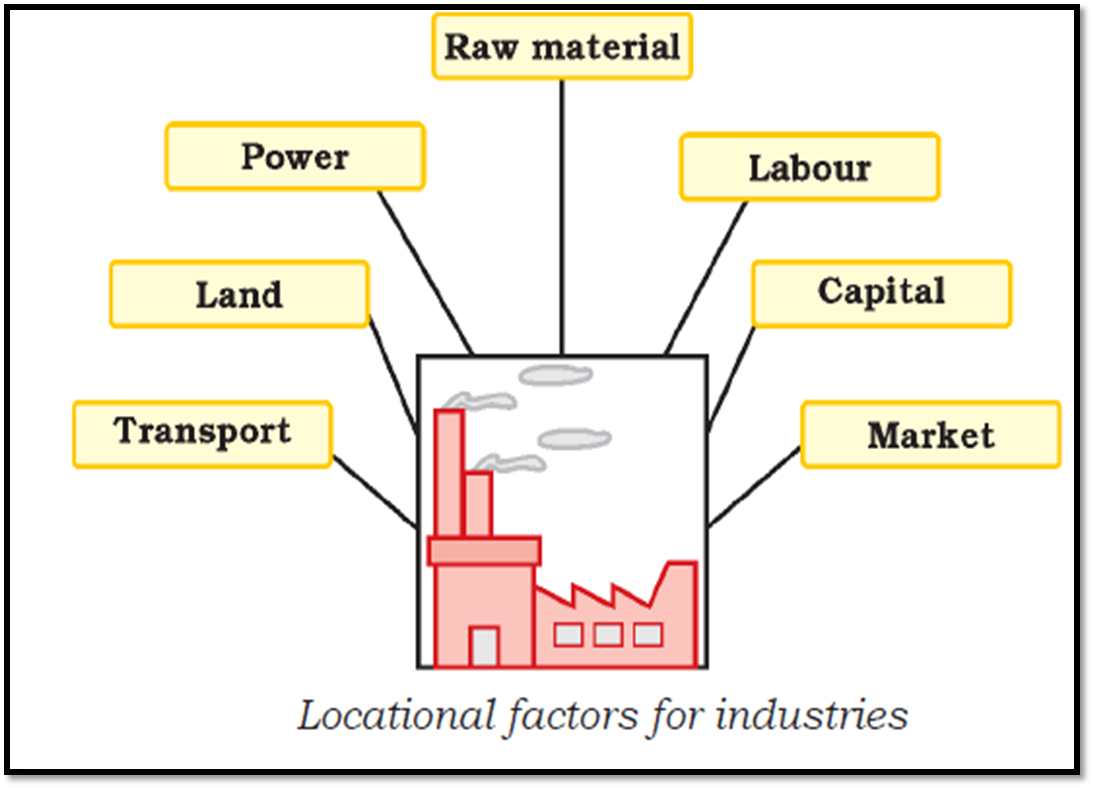
For
ease of convenience, we can classify the location factors into two:
geographical factors and non-geographical factors.
Geographical factors
- Raw Material
- Technology
- Power
- Labor
- Transport
- Storage
and Warehousing.
- Marketing
Feasibility
- Characteristics
of Land and Soil.
- Climate.
- Precipitation
and Water Resources.
- Vulnerability
to Natural Resources.
Non-geographical Factors
- Capital
investment.
- Availability
of loans.
- Investment
climate.
- Government
policies/regulations.
- Influence
of pressure groups.
Explanation:
Capital
or huge investment is needed for the establishment of industries.
Government
policies are another factor that influences industrial location.
The
government sets certain restriction in the allocation of land for industries in
order to reduce regional disparities, to control excessive pollution and to
avoid the excessive clustering of industries in big cities.
The location that has better banking facilities and Insurance are best suited
for the establishment of industries.
Uniformity:
Refers
to the quantity between and within batches of products encompassing the
impurities, excipients and ingredients. The term refers to minimizing variation
between the items or doses, etc.
However,
variations in uniformity post storage are related to the changes in the
drug/product, environment or the packing of the product.
Uniformity
is the foundation of batch processing and manufacturing, and packaging plays a
major role.
Purity:
Refers
not only to the percentage of the active ingredient but also the level of
impurities.
Similar
to how innovative analytical techniques have made the identification of
impurities practical, their elimination has been aided by modern chemical
techniques.
Pharma
packaging helps prevent the drug from exposure to impurities.
Integrity:
Ensures
the package contains the correct product quantity and quality, and that the
package meets necessary specifications and is properly labeled.
Integrity
is all about controlling efficient production and ensuring product quality.
Minimizing
side effects and maintening shelf life are important factors in the process of
manufacturing packaging for pharmaceuticals.
The
type, size, chemical properties, physical properties, material, etc., All
contribute in determining effective packaging
- A
good packaging has the characteristic of not being too heavy nor is it of the
design and size that may create inconvenience to the buyers of products.
So,
convenience is a feature of good package.
Security:
Packaging
to be good must be so done that absolute security for the protection of the
product is assured.
Adaptability:
Packaging
is said to be good where it does not present any difficulty for keeping it in
the almirah or refrigerator.
This
adaptability of packaging is definitely one of its characteristics.
Dependability:
A
good packaging should have such a characteristic that it creates confidence in
the minds of the buyers that the contents must be of standard quality.
Status:
A
good packaging definitely adds prestige to the person who carries products well
packaged.
This
is an additional characteristic that good packaging should have for better
marketing.
Aesthetic:
A good packaging bears the mark of aesthetic sense. This sense adds a lot to
the status of the customer.
A
shelf package or retail package must attract immediate attention.
The
true product story is one of the features of shelf package and this will create
consumer confidence.
The
package should be clean, sanitary with protective seal. Convenience constitutes
one of the most distinguishing features of shelf package and customers must
have the feeling that the packagers have a good value to them.
The
degree of protection required
•
Active pharmaceutical ingredients are usually more stable
than when they are formulated into dosage forms.
•
Decomposition occurs due to the presence of excipients, moisture,
oxygen, light, temperature etc.
•
Degradation of the dosage form can also be as a result of the
formulation process used during formulation.
•
The degree of protection required is a function of the
formulation in question and for this reason; the packaging material used for
photosensitive material should possess the ability to protect the formulation
from light.
•
This is also applicable to hygroscopic, easily oxidized drug
products and so on.
Cost
In
order to make your drugs affordable, cost effectiveness of packaging materials
should be considered.
Manufactures
should endavour not to compromise the integrity of their formulation while
cutting cost rather they should look for a better way to reduce cost which can
by reduction of wastage of packaging material.
Convenience
How
easy is it for a patient to use a formulation in terms of size, weight, method
of opening or reclosing if appropriate during administration of the dosage form
should be considered while choosing packaging material for a dosage form.
Legibility
The
legibility of printing is an important factor to consider while choosing and
designing a package for your formulations as it serves as a source of
information and identification of a formulation as explained in the importance
of giving your product a perfect finish.
Stability Testing and Compatibility Testing
The
stability testing of pharmaceutical products and compatibility testing of
packaging materials is an integral part of R&D in pharmaceutical
industry.
The
stability of a drug in solid and liquid dosage forms depends on the efficacy of
the packaging materials to protect the drug from chemical degradation and
changes in physical characteristics such as appearance, hardness, friability,
dissolution, disintegration, weight variation, moisture contents and mechanical
durability.
This
is particularly necessary for the storage of the products under accelerated
conditions.
It
has been observed that the use of substandard packaging materials by some
pharmaceutical industries leads to stability problems, packaging materials -
drug interaction, poor efficacy to moisture barrier and formation of hazardous
materials
Enhancing
product traceability is one of the critical improvements any company can make
in their supply chain management process.
Traceability
integrates inventory, transportation, and timely delivery while affecting the
overall cost.
For
a long-term customer satisfaction strategy focused on product packaging,
companies need to enhance their traceability and deliver such improvements to
customers through supply chain labelling and packaging.
Increased
costs of supply chain management will end up being paid by the consumer, while
traceability and labeling improvements, on the other hand, might even enhance
sales through packaging enhancement.
All
of these demonstrates value to customers.
Countless
marketing studies lts in many aspects of the supply chain.
It
can increase product efficiency, smoothen the handling of materials at the
production floor, ensure the efficient use of modern supply chain technology
like stackers and pallets, creates better operational activities at both the
plant and the warehouse, and makes for an easier damage control process,
inventory management, cycle counts, and space usage.
Stage S in the Development of a Package Product Combination:
Product
formulation:
All
formulations are required to be documented and stored.
It
is therefore necessary to make certain that all packaging materials are defined
and that all packaging parameters (torque, heat, seal etc) are identified,
controlled and documented (all part of Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Good
Manufacturing Practice (GMP) during formulation studies)
Consideration
of container materials:
It
is important to have a basic knowledge of all packaging materials, their
properties, characteristics etc. and the process by which they are fabricated/
decorated as a packaging container or component, as well as how these and any subsequent
process may affect their properties.
Pack feasibility tests:
This
is the stage where a product is tested in a range of possible package, usually
over a range of conditions from say 200C to 450C, together with alteration in
temperature –humidity range.
In
addition to the storage tests indicated above the immersion of pieces of package
or package components if plastic, in the product or a stimulant i.e. an
extractive-type-test may also be employed.
Extractive
tests are usually mandatory for plastics used for injectables and ophthalmic
products.
Feasibility
tests usually extend over a period of 1-12 months.
Only
after a period of normally 3-6months any decision about the package is taken.
Pre
formulation:
Pre
formulation studies are essential for all packaging components. This provide
information relating to the limitations of the packaging material.
Formal stability test:
Formal
stability test is conducted only after a suitable package –product combination
is selected.
By
conducting the formal stability test, the shelf life of a product can be
determined.
Normally
three large-scale batches of product in each package is selected.
For
long term stability test purpose the temperature is maintained at 250C with a
relative humidity of 60% and in case of accelerated stability test, the
temperature is maintained at 400c with a relative humidity of 75%. The samples
are kept over a period of 5 years and examinations are conducted at the
intervals of 0 (optimal), 3,6,9,12,18,24,30,36,48 and 60 months.
The
data generated are send to the regulatory authorities as part of the marketing
authorization application.
Ongoing
stability:
This
consist of repeated stability on random batches from production in order
confirm that the shelf life does not change during the manufacture of each
batch.
Complaints:
This
is the final means of monitoring the success of the product and pack.
It
is somewhat similar to the monitoring and recording of adverse reactions in
that it is a safeguard to both the company producing the drug and the person
receiving it.
In
all the above tests analytical and packaging technological support is essential
to check both the product and the package.
Qualification and quality control of packaging components:
A
packaging system found acceptable for one drug product is not automatically
assumed to be appropriate for another.
Each
application should contain enough information to show that each proposed
container closure system and its components are suitable for its intended use.
The
type and extent of information that should be provided in an application will
depend on the dosage form and the route of administration.
Protection:
A
container intended to provide protection from light or offered as a
light-resistant container must meet the requirements of the USP<661>
Light Transmission test.
The
procedure requires the use of a spectrophotometer, with the required
sensitivity and accuracy, adapted for measuring the amount of light transmitted
by the plastic materials used for the container.
The
ability of a container closure system to protect against moisture can be
ascertained by performing the USP <661> Water Vapor Permeation test°.
Compatibility:
Components
compatible with a dosage form will not interact sufficiently to change the
quality of the product or its components.
A
leachability study designed to evaluate the amount and/or nature of any
chemical migrating from the plastic material to the pharmaceutical product
should be implemented.
Analytical
techniques such as Liquid Chromatography/ Mass Spectrometry to evaluate
nonvolatile organics, Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) to evaluate
semi volatile organics, and Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) spectroscopy to
detect and quantitate inorganic elements should be a part of this study.
Coupling
MS to LC and GC methods provides a definitive and effective tool for
identifying unknown impurities and degradation products.
Other
changes such as pH shifts, precipitates, and discoloration, which may cause
degradation of pharmaceutical product must be evaluated.
Safety:
All packaging components should be constructed of materials that will not leach
harmful or undesirable amounts of substances to which a patient will be exposed
during drug treatment.
- However, an extraction study should be
one of the first considerations. Isolation is accomplished through sample
preparation, followed by incubation in solvents at well-defined and
well-controlled times and temperatures. - Sample preparation is
an area in which an experienced chemist's knowledge of chemical procedures
is indispensable.
Standard And Specialty Packaging Solution For The
Pharmaceutical Industry:
Traceable
Solutions for Medical Packaging:
The
demand for safety and integrity in the area of medical packaging has taken on
new and significant implications in the past two or three years.
Child
safety, correct dosage, patient traceability, tampering and diversion of
pharmaceuticals are always an area of concern, medical packaging.
Rondo
- fluted trays
For
all low fragile product needs, whether they are made from glass, metal, plastic
or wood, anything that needs special packaging considerations and still should
be clearly visible, with the help of rondo fluted trays.
The
contents can be easily removed and put back after every use.
Coding
in pharmaceutical packaging:
Coding
and marketing have many functions in pharmaceutical packaging.
They
provide expiry dates for products, lot and date codes to aid in tracing and
recalls, bar codes, sales messages and other important information.
Barcodes
can be read by optical scanners called barcode readers or scanned from an image
by special software.
Barcodes
are widely used to implement Auto ID Data Capture (AIDC) systems that improve
the speed and accuracy of computer data entry.
Symbologies:
The
mapping between messages and barcodes is called a symbology.
The
specification of a symbology includes the encoding of the single
digits/characters of the message as well as the start and stop markers into
bars and space, the size of the quiet zone required to be before and after the
barcode as well as the computation of a checksum
Technology of barcodes:
A linear barcode is a binary code (1s and 0s). The lines and
spaces are of varying thickness and printed in different combinations.
To be scanned, there must be accurate printing and adequate
contrast between the bars and spaces.
Scanners employ various technologies to "read"
codes. The two most common forms are lasers and cameras.
Thermal transfer and inkjet printers:
Thermal transfer and inkjet printers are more appropriate
for production line bar code printing.
Specifically, thermal transfer printers produce high
quality, legible and clear bar codes, as well as other types of codes.
Because ink is not involved, there is never any quality
degradation during the process.
Moreover, such printers are virtually maintenance free while
they can also be connected to a software network for record keeping purposes,
which helps with validation.
The main drawback of this technology is that although it can
be set up quickly, it lacks printing speed.
Inkjet Printers:
Inkjet printers are the fastest and least expensive units available on the
market. Unfortunately, there are considerable limitations to what they can
print.
In addition, they require frequent maintenance and can be
quite messy.
Another major downfall is that the print fades after
successive use.
Water-based inkjet fluids tend to streak and blur, while non-water,
soluble inkjet fluids produce a shine that reflects to the scanner and affects
how the bar code is read.
Dot -Matrix printers:
Dot -Matrix printers produce low-quality codes with low contrast, although this
depends on the ribbon used.
Laser printers:
Laser printers are off-line devices requiring a separate label applicator.
They are subjected to toner flaking, meaning that they are
unreliable for long-term bar code printing
Radio frequency identification (RFID)
Radio Frequency
Identification (RFID) It promises a slew of benefits to manufacturers and
retailers alike, including unprecedented control over the supply chain and
enhanced product security.
The technology, called radiofrequency identification, or
RFID, allows manufacturers and distributors to more precisely track drug
products through the supply chain.
RFID makes it easier to ensure that drugs are authentic, and
it also creates an electronic pedigree-a record of the chain of custody from
the point of manufacture to the point of dispensing.
Auto labebooth4556:
Auto Labe's Model 110SR RFID label applicator uses the latest radio frequency
identification (RFID) reader technology for encoding EPC data directly to an
RFID label prior to application.
This is an apply-only solution for customers who do not
require online printing of RFID labels.
The 110SR drive system uses the latest technology to provide
consistent and accurate label placement








0 Comments