Packaging materials in
pharmaceutical industry
• Packaging
is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for
distribution, storage, sale, and use.
• Packaging
also refers to the process of design, evaluation, and production of packages.
• Pharmaceutical
packaging can be defined as the economical means of providing presentation,
protection, identification, information, convenience, compliance, integrity and
stability of the product.
Types of
Packaging
• Primary
packaging- is the material that first envelops the product and holds it.
This is usually the smallest unit of distribution or use. Ex. Aerosol spray
can, blister packs, bottles
• Secondary
packaging - the package external to primary package is known as secondary
package, this package provides additional protection during warehousing and
also provides information about drug product
ex. Boxes, cartons, leaflets
• Tertiary
packaging - It is outer package of secondary packaging & prevents
damage to the products. It is used for bulk handling & shipping.
Characteristics
of Packaging Material
• The
material selected must have the following characteristics
• Must
meet tamper-resistance requirements
• Must
be FDA approved
• Must
be non-toxic
• Must
not impart odor/taste to the product
• Must not reactive with the product
• They
must protect the preparation from environmental conditions
Types of
Packaging Materials Used For Pharmaceutical Packaging
GLASS
• Glass
has been widely used as a drug packaging material.
• Glass is composed of sand, soda ash, limestone,
& cullet.
• Si,
Al, Na, K, Ca, Mg, Zn & Ba are generally used into preparation of glass.
Advantages
• They
are hygienic and suitable for sterilization
• They
are relatively non-reactive ( depending on the grade chosen)
• It can accept a variety of closures
• They
can be used on high speed packaging lines
• They are transparent.
• They
have good protection power.
• They
can be easily labeled.
DISADVANTAGES
• It is relatively heavy
• Glass is fragile so easily broken.
• Release alkali to aqueous preparation
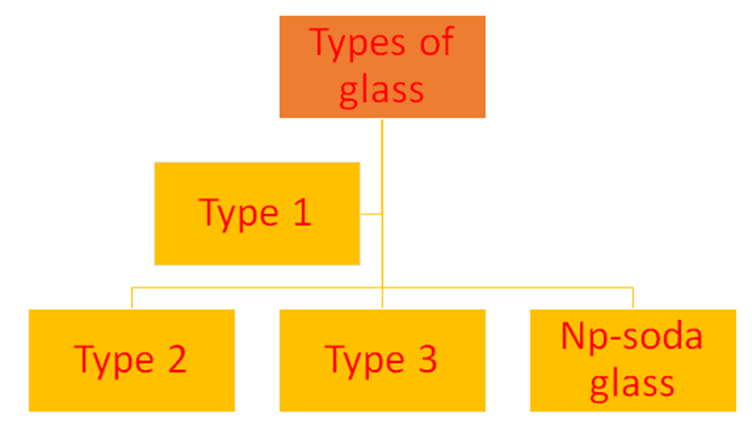
Type of
Glass
• Type
I—Highly resistant borosilicate glass
• Type
II—Treated soda lime glass
• Type III—soda lime glass
• NP—soda
glass (non parenteral usage)
Plastic
• Plastics
may be defined as any group of substances, of natural or synthetic origins,
consisting chiefly of polymers of high molecular weight that can be moulded
into a shape or form by heat and pressure.
Advantages
• Less
weight than glass,
• flexible
• Variety of sizes and shapes
• Essentially
chemically inert, strong, rigid Safety use, high quality, various designs
• Extremely
resistant to breakage
Disadvantages
• Absorption
permeable to moisture
• Poor
printing, thermostatic charge
Types of plastic
Thermosetting
•
When heated they may become flexible but they do
not become liquid
•
e.g. Urea formaldehyde (UF),Phenol formaldehyde
,Melamine formaldehyde (MF), Epoxy resins (epoxides), Polyurethanes (PURs)
Thermoplastics
•
On heating they are soften to viscous fluid
which harden again on cooling.
•
2. e.g. Polyethylene{HDPE – LDPE},
Polyvinylchloride(PVC),Polystyrene Polypropylene, Nylon(PA), Polyethylene
terepthalate(PET) ,Polyvinylidene chloride(PVdC), Polycarbonate Acrylonitrile
butadiene styrene(ABS)
METALS
• Metals
are used for construction of containers. The metals commonly used for this
purpose are aluminium ,tin plated steel, stainless steel, tin and lead
Advantages
• They
are impermeable to light, moisture and gases.
• They
are made into rigid unbreakable containers by impact extrusion.
• They
are light in weight compared to glass containers.
• Labels
can printed directly on to their surface
Disadvantages
• They
are expensive
• They
react with certain chemicals
Types of
Metals
• Tin
containers are preferred for food, pharmaceuticals and any product for which
purity is considered.
• Tin
is the most chemically inert of all collapsible metal tubes
• Lead
has the lowest cost of all tube metals and is widely used for non-food products
such as adhesives, inks. paints and lubricants.
• Lead
should never be used alone for anything taken internally because of the risk
lead poison
• With
internal linings, lead tubes are used for products such as chloride tooth
paste.
• Aluminium
tubes offer significant savings in product shipping costs because of their
light weight
• They
are attractive in nature
RUBBER
• Rubber
is used mainly for the construction of closure meant for vials, transfusion
fluid bottles, dropping bottles and as washers in many other types of product
Types of
Rubber
BUTYL RUBBER
Advantages:
•
Permeability to water vapour .Water absorption
is very low. They are relatively cheaper compared to other synthetic rubbers
Disadvantages:
•
Slow decomposition takes place above 130 ▫ C.
Oil and solvent resistance is not very good
NITRILE RUBBER
Advantages:
•
Oil resistant due to polar nitrile group. Heat
resistant.
Disadvantages:
•
Absorption of bactericide and leaching of
extractives are considerable.
CHLOROPRENE RUBBERS
Advantages:
•
Oil resistant. heat stability is good.
SILICON RUBBERS
Advantages:
•
Heat resistance.Extremely low absorption and
permeability of water. Excellent aging characteristic
Paper
• Paper
and paper boards as packaging material are used to prepre containers as
envelops for dispensing powders,few tablets few capsules etc. of as cartoons
boxes drums for storing large quantity of drugs in an industries.
• They
are mostly used for secondary packging and tertiary packaging
















0 Comments